This came to me as somewhat of a shock, I was bounty hunting at gis.stackexchange
when I came across this question and took a look at the GDAL formats docs.
Apparently, you can't overwrite a raster stored inside a GeoPackage. It's simply not one of the options. But you can however overwrite an existing vector layer with since it's one of the creation options.
So I decided to test it out, if it was really impossible, or just not implemented.
First thing I did was simply look what tables were inside a GeoPackage, and since I'm too lazy to read the standard and the schema I just opened one with good old DBeaver.
Apparently, there are quite a lot of tables in a GeoPackage...
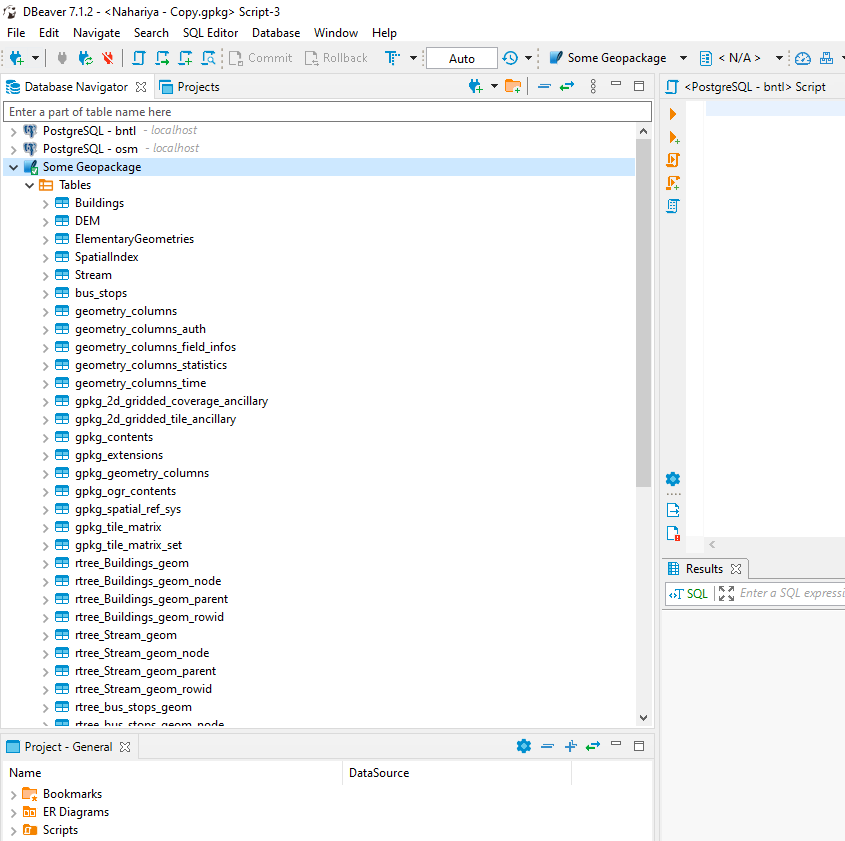
But, did you notice?
A lot of those tables are from the three vector layers inside, so I just looked everywhere else.
And then I started deleting every mention of the `DEM` raster layer (made a point to write down everywhere it was).
<p></p><p>What I came up with was the following code, which enables you to erase and then replace a raster layer from inside a GeoPackage, If you know the name of the layer.</p><p>
</p>
import os
import sqlite3
gpkg = 'path/to/your/db.gpkg'
layer_name= 'superawesomeraster'
# Connect to the GeoPackage
conn = sqlite3.connect(gpkg)
# Delete all mention of the layer
conn.execute('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {}'.format(layer_name))
conn.execute('DELETE FROM gpkg_2d_gridded_coverage_ancillary WHERE tile_matrix_set_name = "{}"'.format(layer_name))
conn.execute('DELETE FROM gpkg_2d_gridded_tile_ancillary WHERE tpudt_name="{}"'.format(layer_name));
conn.execute('DELETE FROM gpkg_tile_matrix WHERE table_name="{}"'.format(layer_name));
conn.execute('DELETE FROM gpkg_tile_matrix_set WHERE table_name="{}"'.format(layer_name));
conn.execute('DELETE FROM gpkg_contents WHERE table_name="{}"'.format(layer_name));
conn.execute('DELETE FROM gpkg_extensions WHERE table_name="{}"'.format(layer_name));
# Commit (Apply) the changes
conn.commit()
# Vacuum the database (optional, but it's always nice to clean up after yourself)
conn.execute('VACUUM')
# Close the connection
conn.close()
# Now you can write a new raster layer in
inputRas = layer_in.source()
outputRas = gpkg
gdal_string = 'gdal_translate -of GPKG "{}" "{}" -co RASTER_TABLE={} -co APPEND_SUBDATASET=YES'.format(inputRas, outputRas,lyr)
os.system(gdal_string)
What this does, is use a simple connection to the GeoPackage (which can be connected to like any other spatialite db) and delete all mention of the table with basic SQL.
Then simply use gdal_translate to write another layer in, in this case a QGIS layer. This part can be replaced with any other way of writing rasters into a GeoPackage, but I find gdal_translate the simplest.
</p>